solo per uso di ricerca
PLX-4720 Inibitore di B-Raf
N. Cat.S1152
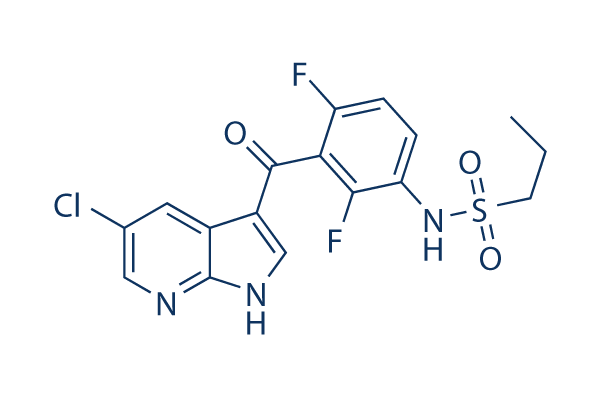
Struttura chimica
Peso molecolare: 413.83
Controllo Qualità
Prodotti spesso usati con PLX-4720
| Target correlati | ERK p38 MAPK JNK MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Altro Raf Inibitori | LY3009120 Exarafenib (KIN-2787) GDC-0879 Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) AZ 628 SB590885 TAK-632 GW5074 RAF265 (CHIR-265) PLX8394 (Plixorafenib, FORE8394) |
Coltura cellulare, trattamento e concentrazione di lavoro
| Linee cellulari | Tipo di saggio | Concentrazione | Tempo di incubazione | Formulazione | Descrizione dellattività | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU-4475 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.07457 μM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.14166 μM | SANGER | |||
| C32 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.15131 μM | SANGER | |||
| M14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.21757 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP50-MEL-B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.29784 μM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.32589 μM | SANGER | |||
| G-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.34637 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-144 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.36329 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38477 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-829 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38968 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-HO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41179 μM | SANGER | |||
| SH-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41422 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.51568 μM | SANGER | |||
| A375 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.67359 μM | SANGER | |||
| MMAC-SF | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.68614 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.70702 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.76148 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.79644 μM | SANGER | |||
| RVH-421 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.86796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.87844 μM | SANGER | |||
| WM-115 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.88692 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.04569 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-679 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.10464 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ7-mel | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.14963 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.33386 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.6086 μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66294 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.04978 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.11969 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.30787 μM | SANGER | |||
| PA-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.72673 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.87946 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.92232 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.40176 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.55266 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP66-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.15927 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.49179 μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.53325 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2058 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.72164 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.73908 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8305C | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.1873 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-7951 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.80283 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.97603 μM | SANGER | |||
| TI-73 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.00902 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1080 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.10946 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.14924 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8-MG-BA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.18129 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21373 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.22493 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.45423 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.81931 μM | SANGER | |||
| BCPAP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.21764 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.36907 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-741 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.01679 μM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.07068 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.41516 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.75314 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.05178 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.56999 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6048 μM | SANGER | |||
| VA-ES-BJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.0149 μM | SANGER | |||
| A431 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4212 μM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.458 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8472 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.2404 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-HEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.3527 μM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7178 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.2655 μM | SANGER | |||
| TYK-nu | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.3932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NMC-G1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6062 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.7169 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.8833 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-566MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9576 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-140 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.0753 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3359 μM | SANGER | |||
| U251 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.8492 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-542MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9222 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.2684 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4293 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4305 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4458 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7616 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7835 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ2-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.0646 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-12T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.4862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KE-37 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8107 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-411N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.118 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2228 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4965 μM | SANGER | |||
| HN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.7248 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.818 μM | SANGER | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.3172 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5708 μM | SANGER | |||
| YKG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5711 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-81-FD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5858 μM | SANGER | |||
| 23132-87 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.7642 μM | SANGER | |||
| NUGC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.9887 μM | SANGER | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.0478 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1755 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.4764 μM | SANGER | |||
| RH-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.5748 μM | SANGER | |||
| RXF393 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.6756 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-134-A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7056 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7201 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.1915 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGR-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.3796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-92 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.4987 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MES-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.7381 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.8624 μM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.1203 μM | SANGER | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.244 μM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5155 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6059 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MEL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6751 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7366 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7979 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.0817 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.6412 μM | SANGER | |||
| J-RT3-T3-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.7595 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.8744 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.0023 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.2751 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.3192 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.938 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-449 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2018 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2813 μM | SANGER | |||
| LOXIMVI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.368 μM | SANGER | |||
| GR-ST | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.6706 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.944 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.1604 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.2814 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.713 μM | SANGER | |||
| EGI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8845 μM | SANGER | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.9272 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB996-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.5682 μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-97TM1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.1964 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3301 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.5973 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1770 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.1648 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6504 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.7236 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8385 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8544 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8971 μM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.7292 μM | SANGER | |||
| U031 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8132 μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.0774 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.6455 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1155 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0015 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1793 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1026 μM | SANGER | |||
| P30-OHK | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1332 μM | SANGER | |||
| AN3-CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1615 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-257 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.79 μM | SANGER | |||
| MCF7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.8629 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4285 μM | SANGER | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4957 μM | SANGER | |||
| HGC-27 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1092 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.2895 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.9959 μM | SANGER | |||
| 786-0 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.65 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.0359 μM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.1778 μM | SANGER | |||
| EFM-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7533 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7806 μM | SANGER | |||
| UM-UC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.8059 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-29 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.8792 μM | SANGER | |||
| LN-405 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.0827 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.7726 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-502MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.9676 μM | SANGER | |||
| GMS-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.2974 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-JUSO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.347 μM | SANGER | |||
| insect cells | Function assay | Inhibition of N-terminal His-tagged BRAF V600E mutant (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells co-expressing CDC37 using biotinylated-MEK as substrate by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.013 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of BRAF V600E mutant in human A375 cells assessed as reduction in ERK phosphorylation by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.044 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of b-Raf in human A375 cells assessed phosphorylation of ERK, IC50 = 0.046 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human A375 cells expressing B-Raf V600E mutant and wild type Ras, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A375 cells harboring BRAF V600E mutant after 72 hrs by CellTiter-Glo assay, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 29461827 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells expressing wild type b-Raf and KRAS mutant, IC50 = 27 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Clicca per visualizzare più dati sperimentali sulle linee cellulari | ||||||
Informazioni chimiche, conservazione e stabilità
| Peso molecolare | 413.83 | Formula | C17H14ClF2N3O3S |
Conservazione (Dalla data di ricezione) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. CAS | 918505-84-7 | Scarica SDF | Conservazione delle soluzioni stock |
|
|
| Sinonimi | N/A | Smiles | CCCS(=O)(=O)NC1=C(C(=C(C=C1)F)C(=O)C2=CNC3=C2C=C(C=N3)Cl)F | ||
Solubilità
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(200.56 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calcolatore di Molarità
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calcolatore di formulazione in vivo (Soluzione chiara)
Passo 1: Inserire le informazioni di seguito (Consigliato: Un animale aggiuntivo per tenere conto della perdita durante lesperimento)
Passo 2: Inserire la formulazione in vivo (Questo è solo il calcolatore, non la formulazione. Contattateci prima se non cè una formulazione in vivo nella sezione Solubilità.)
Risultati del calcolo:
Concentrazione di lavoro: mg/ml;
Metodo per preparare il liquido master di DMSO: mg farmaco predissolto in μL DMSO ( Concentrazione del liquido master mg/mL, Vi preghiamo di contattarci prima se la concentrazione supera la solubilità del DMSO del lotto del farmaco. )
Metodo per preparare la formulazione in vivo: Prendere μL DMSO liquido master, quindi aggiungereμL PEG300, mescolare e chiarire, quindi aggiungereμL Tween 80, mescolare e chiarire, quindi aggiungere μL ddH2O, mescolare e chiarire.
Metodo per preparare la formulazione in vivo: Prendere μL DMSO liquido master, quindi aggiungere μL Olio di mais, mescolare e chiarire.
Nota: 1. Si prega di assicurarsi che il liquido sia limpido prima di aggiungere il solvente successivo.
2. Assicurarsi di aggiungere il/i solvente/i in ordine. È necessario assicurarsi che la soluzione ottenuta, nellaggiunta precedente, sia una soluzione limpida prima di procedere allaggiunta del solvente successivo. Metodi fisici come il vortex, gli ultrasuoni o il bagno dacqua calda possono essere utilizzati per facilitare la dissoluzione.
Meccanismo dazione
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
C-Raf-1 (Y340D/Y341D)
(Cell-free assay) 6.7 nM
B-Raf (V600E)
(Cell-free assay) 13 nM
BRK
(Cell-free assay) 130 nM
B-Raf
(Cell-free assay) 160 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
PLX-4720 mostra una selettività >10 volte superiore contro il B-Raf wild type e una selettività >100 volte superiore rispetto ad altre chinasi come Frk, Src, Fak, FGFR e Aurora A con IC50 di 1,3-3,4 μM. Questo composto inibisce significativamente la fosforilazione di ERK in linee cellulari che esprimono B-RafV600E con IC50 di 14-46 nM, ma non nelle cellule con B-Raf wild-type. Inibisce significativamente la crescita di linee cellulari tumorali che esprimono l'oncogene B-RafV600E, come COLO205, A375, WM2664 e COLO829 con GI50 di 0,31 μM, 0,50 μM, 1,5 μM e 1,7 μM, rispettivamente. Inoltre, questo trattamento chimico a 1 μM induce l'arresto del ciclo cellulare e l'apoptosi esclusivamente nelle cellule 1205Lu positive per B-RafV600E, ma non nelle cellule C8161 wild-type per B-Raf. Questo trattamento con il composto (10 μM) induce significativamente un'espressione di BIM >14 volte nelle cellule PTEN+, rispetto alle linee cellulari PTEN- (4 volte), fornendo una spiegazione della resistenza delle cellule PTEN- a questa apoptosi indotta da sostanze chimiche.
|
| Saggio chinasico |
Attività chinasiche di Raf in vitro
|
|
Le attività chinasiche in vitro del Raf wild type e dei mutanti sono determinate misurando la fosforilazione della proteina MEK biotinilata utilizzando la tecnologia AlphaScreen di Perkin-Elmer. Per ogni enzima (0,1 ng), vengono eseguite reazioni di 20 μL in 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0,01% Tween-20, 100 nM di proteina biotin-MEK, varie concentrazioni di ATP e concentrazioni crescenti di PLX-4720 a temperatura ambiente. Le reazioni vengono interrotte a 2, 5, 8, 10, 20 e 30 minuti con 5 μL di una soluzione contenente 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 200 mM NaCl, 80 mM EDTA e 0,3% BSA. La soluzione di interruzione include anche l'anticorpo phospho-MEK, perline donatrici rivestite di streptavidina e perline accettrici di proteina A dal kit di rilevazione di proteina A AlphaScreen. L'anticorpo e le perline vengono pre-incubati nella soluzione di interruzione al buio a temperatura ambiente per 30 minuti. La diluizione finale dell'anticorpo è 1/2.000 e la concentrazione finale di ogni perlina è 10 μg/mL. Le piastre del saggio vengono incubate a temperatura ambiente per un'ora e quindi lette su un lettore AlphaQuest di PerkinElmer.
|
|
| In vivo |
La somministrazione orale di PLX-4720 a 20 mg/kg/giorno induce significativi ritardi e regressioni della crescita tumorale in xenotrapianti tumorali COLO205 dipendenti da B-RafV600E, senza evidenti effetti avversi nei topi anche a una dose di 1 g/kg. Questo composto a 100 mg/kg due volte al giorno elimina quasi completamente gli xenotrapianti 1205Lu che esprimono B-RafV600E, mentre non ha attività contro gli xenotrapianti C8161 che esprimono B-Raf wild-type. Gli effetti antitumorali di questo composto correlano con il blocco della via MAPK in quelle cellule che ospitano la mutazione V600E. Questo trattamento chimico a 30 mg/kg/giorno inibisce significativamente la crescita tumorale degli xenotrapianti 8505c di >90% e diminuisce drasticamente le metastasi polmonari distanti.
|
Riferimenti |
|
Applicazioni
| Metodi | Biomarcatori | Immagini | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-FAK(S910) p-EGFR 1173 / EGFR / p-Akt / Akt p27 / Cyclin D1 / pRb pAkt(Ser473) / pAkt(Thr308) |
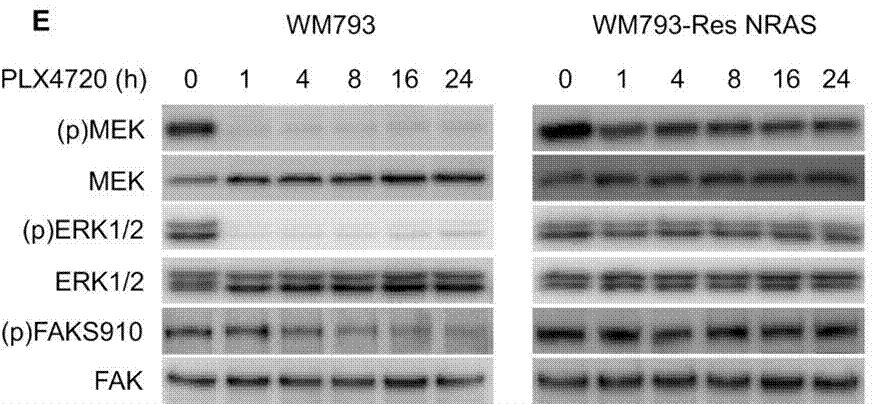
|
23076151 |
| Immunofluorescence | LAMP1 ZKSCAN3 / TFEB |
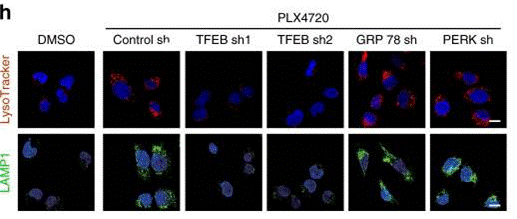
|
30979895 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
27848137 |
| ELISA | mIFN-γ |
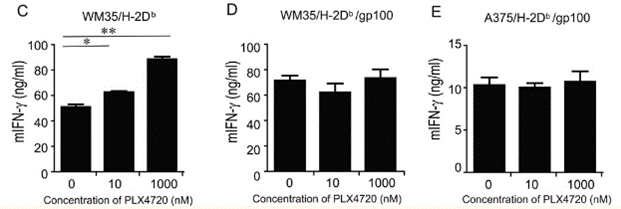
|
23204132 |
Supporto tecnico
Istruzioni per la manipolazione
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Per qualsiasi altra domanda, si prega di lasciare un messaggio.
Domande Frequenti
Domanda 1:
What would you recommend to make working solution for intraperitoneal injection into mice?
Risposta:
Due to its very limited solubility in aqueous solution, this compound can be administered as a not fully dissolved suspension via oral gavage. For this reason, we recommend oral gavage for its administration.
