solo per uso di ricerca
Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585) Dihydrochloride HDAC inibitore
N. Cat.S1096
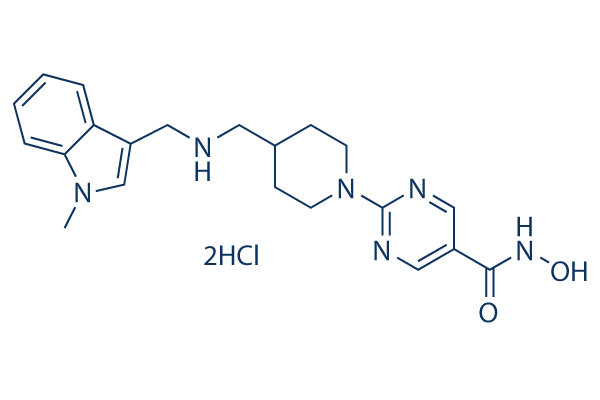
Struttura chimica
Peso molecolare: 467.39
Controllo Qualità
Coltura cellulare, trattamento e concentrazione di lavoro
| Linee cellulari | Tipo di saggio | Concentrazione | Tempo di incubazione | Formulazione | Descrizione dellattività | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 cells | Cell viability assay | 24, 48, or 72 h | the IC50 values of cells for 48 and 72 h of quisinostat treatment were 82.4 and 42.0 nM, respectively. | 27423454 | ||
| RH30 cells | Function assay | 15 nM | 24 h and 30 h | GSK690 and JNJ-26481585 cooperated to induce cleavage of the initiator caspase-9 into its active p35 and p37 fragments and of the effector caspase-3 into its active p12 and p17 fragments | 28617441 | |
| RD cells | Function assay | 15 nM | 24 h and 30 h | GSK690 and JNJ-26481585 cooperated to induce cleavage of the initiator caspase-9 into its active p35 and p37 fragments and of the effector caspase-3 into its active p12 and p17 fragments | 28617441 | |
| HepG2 | Cell viability assay | 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 and 320 nM | 24, 48, 72 h | The IC50 values of cells for quisinostat treatment at 48 and 72 h were 81.2 and 30.8 nM, respectively. | 28849080 | |
| HuT78 | Function assay | 10 nM | increases the level of acetylated lysine K10 of histone H3 | 30012418 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC1 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.00011 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC2 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.00033 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC3/NCOR2 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.00486 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| HUT78 | Function assay | 18 hrs | Pro-apoptotic activity in human HUT78 cells after 18 hrs by caspase-Glo 3/7 assay, EC50 = 0.0065 μM. | 30122227 | ||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Binding affinity to human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells by ITC method, Kd = 0.0227 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Binding affinity to Schistosoma mansoni His-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells by ITC method, Kd = 0.0284 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.0644 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC6 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.0768 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL6 mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.093 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL1/mL6 mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.094 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL6/L179I mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.169 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL1/mL6/L179I mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.217 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of Schistosoma mansoni His-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.3034 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Daoy | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for Daoy cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Clicca per visualizzare più dati sperimentali sulle linee cellulari | ||||||
Informazioni chimiche, conservazione e stabilità
| Peso molecolare | 467.39 | Formula | C21H28Cl2N6O2 |
Conservazione (Dalla data di ricezione) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. CAS | 875320-31-3 | -- | Conservazione delle soluzioni stock |
|
|
| Sinonimi | N/A | Smiles | CN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)CNCC3CCN(CC3)C4=NC=C(C=N4)C(=O)NO.Cl.Cl | ||
Solubilità
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 79 mg/mL
(169.02 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calcolatore di Molarità
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calcolatore di formulazione in vivo (Soluzione chiara)
Passo 1: Inserire le informazioni di seguito (Consigliato: Un animale aggiuntivo per tenere conto della perdita durante lesperimento)
Passo 2: Inserire la formulazione in vivo (Questo è solo il calcolatore, non la formulazione. Contattateci prima se non cè una formulazione in vivo nella sezione Solubilità.)
Risultati del calcolo:
Concentrazione di lavoro: mg/ml;
Metodo per preparare il liquido master di DMSO: mg farmaco predissolto in μL DMSO ( Concentrazione del liquido master mg/mL, Vi preghiamo di contattarci prima se la concentrazione supera la solubilità del DMSO del lotto del farmaco. )
Metodo per preparare la formulazione in vivo: Prendere μL DMSO liquido master, quindi aggiungereμL PEG300, mescolare e chiarire, quindi aggiungereμL Tween 80, mescolare e chiarire, quindi aggiungere μL ddH2O, mescolare e chiarire.
Metodo per preparare la formulazione in vivo: Prendere μL DMSO liquido master, quindi aggiungere μL Olio di mais, mescolare e chiarire.
Nota: 1. Si prega di assicurarsi che il liquido sia limpido prima di aggiungere il solvente successivo.
2. Assicurarsi di aggiungere il/i solvente/i in ordine. È necessario assicurarsi che la soluzione ottenuta, nellaggiunta precedente, sia una soluzione limpida prima di procedere allaggiunta del solvente successivo. Metodi fisici come il vortex, gli ultrasuoni o il bagno dacqua calda possono essere utilizzati per facilitare la dissoluzione.
Meccanismo dazione
| Caratteristiche |
An orally bioavailable, second-generation, hydroxamic acid-based HDAC inhibitor.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HDAC1
(Cell-free assay) 0.11 nM
HDAC2
(Cell-free assay) 0.33 nM
HDAC11
(Cell-free assay) 0.37 nM
HDAC10
(Cell-free assay) 0.46 nM
HDAC4
(Cell-free assay) 0.64 nM
HDAC5
(Cell-free assay) 3.69 nM
HDAC8
(Cell-free assay) 4.26 nM
HDAC3
(Cell-free assay) 4.86 nM
|
| In vitro |
JNJ-26481585 mostra un'ampia attività antiproliferativa in linee cellulari di cancro solido ed ematologico, come tutte le linee cellulari di tumore polmonare, mammario, del colon, della prostata, cerebrale e ovarico, con IC50 che vanno da 3,1 a 246 nM, il che è più potente di R306465, CRA-24781 o mocetinostat in varie linee cellulari di cancro umano testate. Uno studio recente mostra che JNJ-26481585 promuove la morte delle cellule di mieloma a basse concentrazioni nanomolari, risultando in deplezione di Mcl-1 e induzione di Hsp72. |
| Saggio chinasico |
Saggi di attività HDAC
|
|
In tutti i casi, le proteine HDAC a lunghezza intera sono espresse utilizzando cellule Sf9 infettate da baculovirus. Inoltre, HDAC3 è coespressa come un complesso con NCOR2 umana. Per valutare l'attività dei complessi cellulari contenenti HDAC1, i complessi HDAC1 immunoprecipitati vengono incubati con un frammento di peptide di istone H4 marcato con [3H]acetile [biotina-(6-aminoesanoico)Gly-Ala-(acetil[3H])Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-NH2] in un volume totale di 50μL di tampone di saggio enzimatico (25mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 1 M saccarosio, 0.1 mg/mL BSA e 0.01% (v/v) Triton X-100). L'incubazione viene eseguita per 45 minuti a 37 °C (immunoprecipitati) o 30 minuti a temperatura ambiente. Prima dell'aggiunta del substrato, gli inibitori di HDAC vengono aggiunti a concentrazioni crescenti e preincubati per 10 minuti a temperatura ambiente. Dopo l'incubazione, la reazione viene interrotta con 35μL di tampone di arresto (1 M HCl e 0.4 M acido acetico). L'acido [3H]acetico rilasciato viene estratto con 800μL di acetato di etile e quantificato mediante conteggio di scintillazione. Quantità uguali di HDAC1 sono immunoprecipitate come indicato dall'analisi Western blot. I risultati dell'attività di HDAC1 sono presentati come media ± DS di tre esperimenti indipendenti su un singolo lisato.
|
|
| In vivo |
In un modello di screening di tumore ovarico A2780 responsivo a HDAC1, la somministrazione di JNJ-26481585 alla sua dose massima tollerata (10 mg/kg i.p. e 40 mg/kg p.o.) per 3 giorni porta a una fluorescenza regolata da HDAC1, che predice l'inibizione della crescita tumorale. Inoltre, JNJ-26481585 mostra anche effetti inibitori più potenti sulla crescita delle metastasi epatiche colorettali C170HM2. |
Riferimenti |
|
Applicazioni
| Metodi | Biomarcatori | Immagini | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
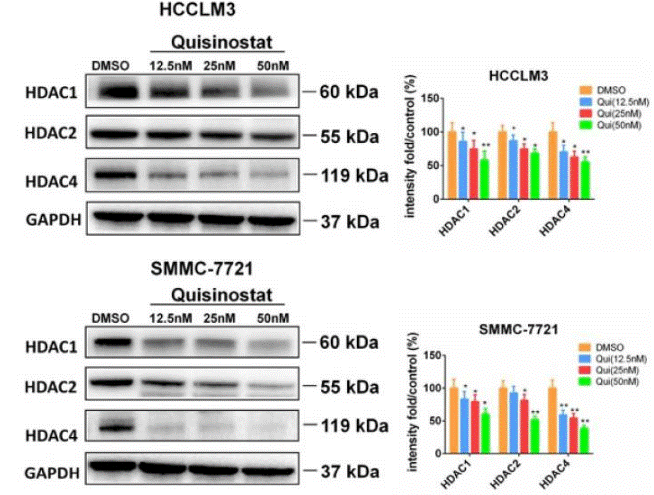
| Western blot | HDAC1 / HDAC2 / HDAC4 p21 / CDK2 / CDK4 / CDK6 / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin E1 / Cyclin A2 Caspase-3/ Cleaved caspase-3 / caspase-9 / Cleaved caspase-9 / PARP / Cleaved PARP / Bcl-xl / Bcl2 / Bax / Survivin PI3K-p110 / PI3K-p85 / p-AKT / JNK / p-JNK / p-c-Jun |
|
30443188 |
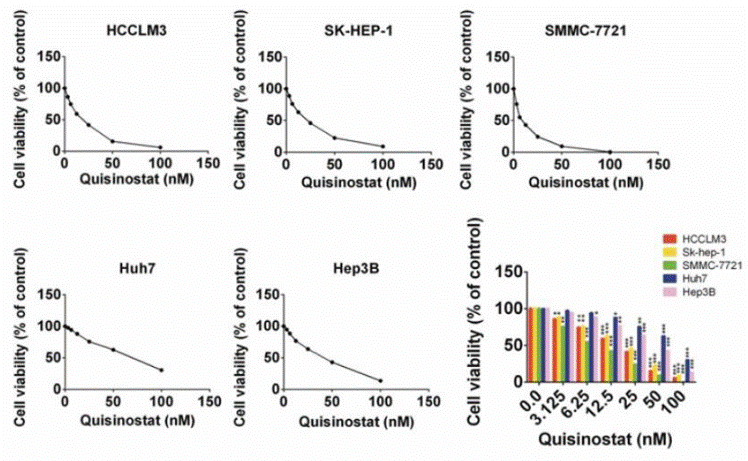
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
30443188 |
Informazioni sullo studio clinico
(dati da https://clinicaltrials.gov, aggiornato il 2024-05-22)
| Numero NCT | Reclutamento | Condizioni | Sponsor/Collaboratori | Data di inizio | Fasi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02948075 | Completed | Ovarian Cancer |
NewVac LLC|Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. Belgium |
September 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01464112 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma |
Janssen Research & Development LLC |
September 16 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00676728 | Terminated | Advanced or Refractory Leukemia|Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development L.L.C. |
December 2008 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00677105 | Completed | Lymphoma|Neoplasms |
Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development L.L.C.|Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. Belgium |
August 2007 | Phase 1 |
Supporto tecnico
Istruzioni per la manipolazione
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Per qualsiasi altra domanda, si prega di lasciare un messaggio.
Domande Frequenti
Domanda 1:
I was thinking of resuspending it in 10% hydroxy-propyl-β-cyclodextrin, 25mg/ml mannitol, in sterile water (final pH 8.7). Is this a good vehicle to use? What is the solubility of this compound in such a vehicle?
Risposta:
This vehicle can be used for in vivo studies. The following papers also used this vehicle: 1. http://www.nature.com/leu/journal/v23/n10/full/leu2009121a.html; 2. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/69/13/5307.long (The solvent contains 10% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, 0.8% HCl (0.1 N), 0.9 % NaOH (0.1 N), 3.4% mannitol and pyrogen-free water). Its solubility is 2mg/ml.
