réservé à la recherche
PF-562271 Besylate FAK inhibiteur
N° Cat.S2672
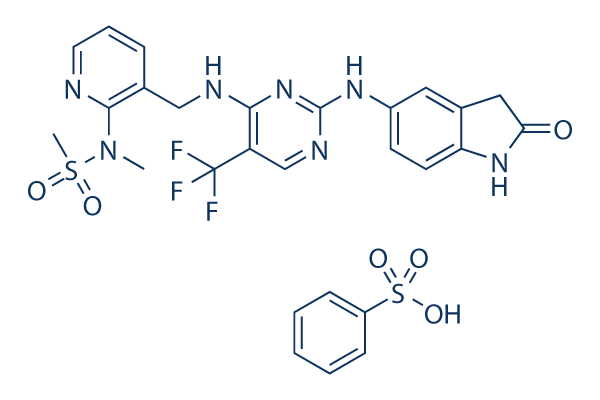
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 665.66
Contrôle qualité
| Cibles apparentées | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR Src HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Autre FAK Inhibiteurs | Defactinib (VS-6063) PF-562271 (VS-6062) PF-573228 VS-4718 (PND-1186) PF-562271 HCl TAE226 (NVP-TAE226) GSK2256098 PF-431396 Y15 Solanesol (Nonaisoprenol) |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MV-4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MV-4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.2766 μM | ||||
| human SW982 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW982 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.3282 μM | ||||
| human KM12 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KM12 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.38557 μM | ||||
| human COLO-205 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human COLO-205 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.48658 μM | ||||
| human COLO-829 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human COLO-829 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.76176 μM | ||||
| human MG-63 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MG-63 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.80637 μM | ||||
| human IGROV-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IGROV-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.81038 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H650 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H650 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.83154 μM | ||||
| human RT-112 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RT-112 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.9846 μM | ||||
| human BCPAP cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BCPAP cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.01288 μM | ||||
| ALL-PO cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ALL-PO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.01584 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-270 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-270 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.04714 μM | ||||
| human 8305C cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human 8305C cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.09904 μM | ||||
| NCI-H810 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H810 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.10776 μM | ||||
| human CAL-33 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-33 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.12938 μM | ||||
| human AN3-CA cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AN3-CA cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.21867 μM | ||||
| human NKM-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NKM-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.27506 μM | ||||
| human BPH-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BPH-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.28766 μM | ||||
| human MES-SA cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MES-SA cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.30682 μM | ||||
| human CAL-62 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-62 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.31909 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-150 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-150 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.35236 μM | ||||
| human SK-UT-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-UT-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.44647 μM | ||||
| human HUTU-80 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HUTU-80 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.44886 μM | ||||
| human SIG-M5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SIG-M5 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.48487 μM | ||||
| human AGS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AGS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.52124 μM | ||||
| human ST486 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ST486 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.53278 μM | ||||
| human HSC-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HSC-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.5395 μM | ||||
| human BC-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BC-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.61664 μM | ||||
| human CGTH-W-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CGTH-W-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.61679 μM | ||||
| human MZ1-PC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MZ1-PC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.62312 μM | ||||
| human SW1710 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1710 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.62628 μM | ||||
| human EW-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EW-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.63466 μM | ||||
| human U251 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human U251 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.74031 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H460 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H460 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.04839 μM | ||||
| human DU-4475 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-4475 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.14759 μM | ||||
| human MFE-296 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MFE-296 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.47792 μM | ||||
| human DU-145 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.49118 μM | ||||
| human MDA-MB-231 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.49572 μM | ||||
| human SNU-387 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SNU-387 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.5282 μM | ||||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur les lignées cellulaires | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 665.66 | Formule | C21H20F3N7O3S.C6H6O3S |
Stockage (À partir de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 939791-38-5 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | PF-00562271 Besylate | Smiles | CN(C1=C(C=CC=N1)CNC2=NC(=NC=C2C(F)(F)F)NC3=CC4=C(C=C3)NC(=O)C4)S(=O)(=O)C.C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)O | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
4-Methylpyridine : 25 mg/mL
DMSO
: 0.4 mg/mL
(0.6 mM)
Water : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Entrez les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Entrez la formulation in vivo (Ceci nest que le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, ajouter ensuiteμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, ajouter ensuiteμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, ajouter ensuite μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, ajouter ensuite μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Remarque : 1. Assurez-vous que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue lors de lajout précédent est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
FAK
(Cell-free assay) 1.5 nM
PYK2
(Cell-free assay) 13 nM
CDK2/CyclinE
(Cell-free assay) 30 nM
CDK3/CyclinE
(Cell-free assay) 47 nM
CDK1/CyclinB
(Cell-free assay) 58 nM
CDK7/CyclinH/MAT1
(Cell-free assay) 97 nM
FLT3
(Cell-free assay) 97 nM
GSK-3α
(Cell-free assay) 101 nM
CDK5/p35
(Cell-free assay) 120 nM
GSK-3β
(Cell-free assay) 133 nM
Aurora A
(Cell-free assay) 145 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Le PF-562271 Besylate montre des effets inhibiteurs sélectifs sur l'activité tyrosine kinase de FAK et Pyk2 avec des IC50 de 1,5 nM et 14 nM, respectivement. Et dans des tests basés sur des cellules, l'IC50 du PF-562271 est de 5 nM pour FAK, ce qui est plus sélectif par rapport à d'autres cibles kinases. Dans les cultures bidimensionnelles (2D), le PF-562271 entraîne une inhibition dose-dépendante de la prolifération cellulaire dans les cellules FAK WT, FAK−/− et FAK déficientes en kinase (KD) avec des IC50 de 3,3 μM, 2,08 μM et 2,01 μM, respectivement.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Test de kinase recombinante et cinétique enzymatique
|
|
En bref, le domaine kinase FAK purifié et activé (acides aminés 410–689) est mis à réagir avec 50 μM d'ATP et 10 μg par puits d'un polymère peptidique aléatoire de Glu et Tyr, p(Glu/Tyr), dans un tampon kinase [50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 125 mM NaCl et 48 mM MgCl2] pendant 15 minutes. La phosphorylation de p(Glu/Tyr) est contestée avec du PF-562271 dilué en série à des concentrations de 1/2-Log, en commençant par une concentration maximale de 1 μM. Chaque concentration est testée en triple. La phosphorylation de p(Glu/Tyr) est détectée avec un anticorps anti-phospho-tyrosine (PY20) général suivi d'un anticorps de chèvre anti-souris IgG conjugué à la peroxydase de raifort (HRP). Le substrat HRP est ajouté, et les lectures d'absorbance à 450 nm sont obtenues après l'ajout de la solution d'arrêt (2 M H2SO4). Les valeurs d'IC50 sont déterminées à l'aide du modèle Hill-Slope. Le profilage de la sélectivité kinase à large spectre est réalisé en interne et en utilisant le service de criblage de sélectivité KinaseProfiler disponible via UpState Biotechnology.
|
|
| In vivo |
Dans plusieurs modèles de xénogreffes s.c. humaines, le PF-562271 présente une inhibition dose-dépendante de la croissance tumorale et produit une inhibition tumorale maximale pour PC-3M, BT474, BxPc3 et LoVo, allant de 78 % à 94 % d'inhibition à des doses de 25 à 50 mg/kg deux fois par jour, sans perte de poids, morbidité ou décès. Le PF-562271 (25 mg/kg par voie orale) entraîne une diminution significative de la progression tumorale dans les modèles de xénogreffes PC3M-luc-C6 à la fois sous-cutanées et de métastases osseuses. Dans un modèle de xénogreffe de carcinome hépatocellulaire Huh7.5, la thérapie combinée de sunitinib et PF-562271 cible Angiogenesis et l'agressivité tumorale, et produit un effet anti-tumoral plus significatif qu'un agent unique en bloquant la croissance tumorale et en affectant la capacité de la tumeur à récupérer après l'arrêt de la thérapie.
|
Références |
|
Informations sur lessai clinique
(données de https://clinicaltrials.gov, mis à jour le 2024-05-22)
| Numéro NCT | Recrutement | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborateurs | Date de début | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00666926 | Completed | Head and Neck Neoplasm|Prostatic Neoplasm|Pancreatic Neoplasm |
Verastem Inc. |
December 2005 | Phase 1 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
Questions fréquemment posées
Question 1:
We are planning both in vitro and in vivo experiments and want to know how to reconstitute it for these purposes?
Réponse :
It has poor solubility in DMSO and water, with solubility in DMSO being only 0.4mg/ml. In a previous literature report (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18339875), the author used 5% Gelucire to formulate this compound. You can also consider other co-solvents such as PEG400, CMC, Tween80, and Captisol.
Question 2:
Can you provide with a few common vehicles for it, S2672 for use as oral gavage?
Réponse :
It can be dissolved in 0.5% CMC Na at 30 mg/ml as a suspension. If 4% DMSO can be used in your experiment, it will help dissolving the suspension more homogeneously.
