réservé à la recherche
PLX-4720 Inhibiteur de B-Raf
N° Cat.S1152
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 413.83
Contrôle qualité
Produits Souvent Utilisés Avec PLX-4720
| Cibles apparentées | ERK p38 MAPK JNK MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Autre Raf Inhibiteurs | LY3009120 Exarafenib (KIN-2787) GDC-0879 Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) AZ 628 SB590885 TAK-632 GW5074 RAF265 (CHIR-265) PLX8394 (Plixorafenib, FORE8394) |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU-4475 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.07457 μM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.14166 μM | SANGER | |||
| C32 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.15131 μM | SANGER | |||
| M14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.21757 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP50-MEL-B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.29784 μM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.32589 μM | SANGER | |||
| G-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.34637 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-144 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.36329 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38477 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-829 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38968 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-HO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41179 μM | SANGER | |||
| SH-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41422 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.51568 μM | SANGER | |||
| A375 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.67359 μM | SANGER | |||
| MMAC-SF | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.68614 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.70702 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.76148 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.79644 μM | SANGER | |||
| RVH-421 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.86796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.87844 μM | SANGER | |||
| WM-115 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.88692 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.04569 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-679 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.10464 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ7-mel | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.14963 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.33386 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.6086 μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66294 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.04978 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.11969 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.30787 μM | SANGER | |||
| PA-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.72673 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.87946 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.92232 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.40176 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.55266 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP66-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.15927 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.49179 μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.53325 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2058 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.72164 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.73908 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8305C | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.1873 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-7951 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.80283 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.97603 μM | SANGER | |||
| TI-73 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.00902 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1080 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.10946 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.14924 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8-MG-BA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.18129 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21373 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.22493 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.45423 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.81931 μM | SANGER | |||
| BCPAP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.21764 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.36907 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-741 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.01679 μM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.07068 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.41516 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.75314 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.05178 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.56999 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6048 μM | SANGER | |||
| VA-ES-BJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.0149 μM | SANGER | |||
| A431 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4212 μM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.458 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8472 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.2404 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-HEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.3527 μM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7178 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.2655 μM | SANGER | |||
| TYK-nu | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.3932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NMC-G1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6062 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.7169 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.8833 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-566MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9576 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-140 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.0753 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3359 μM | SANGER | |||
| U251 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.8492 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-542MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9222 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.2684 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4293 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4305 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4458 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7616 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7835 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ2-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.0646 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-12T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.4862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KE-37 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8107 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-411N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.118 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2228 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4965 μM | SANGER | |||
| HN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.7248 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.818 μM | SANGER | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.3172 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5708 μM | SANGER | |||
| YKG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5711 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-81-FD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5858 μM | SANGER | |||
| 23132-87 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.7642 μM | SANGER | |||
| NUGC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.9887 μM | SANGER | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.0478 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1755 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.4764 μM | SANGER | |||
| RH-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.5748 μM | SANGER | |||
| RXF393 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.6756 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-134-A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7056 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7201 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.1915 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGR-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.3796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-92 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.4987 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MES-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.7381 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.8624 μM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.1203 μM | SANGER | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.244 μM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5155 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6059 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MEL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6751 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7366 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7979 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.0817 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.6412 μM | SANGER | |||
| J-RT3-T3-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.7595 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.8744 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.0023 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.2751 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.3192 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.938 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-449 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2018 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2813 μM | SANGER | |||
| LOXIMVI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.368 μM | SANGER | |||
| GR-ST | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.6706 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.944 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.1604 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.2814 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.713 μM | SANGER | |||
| EGI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8845 μM | SANGER | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.9272 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB996-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.5682 μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-97TM1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.1964 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3301 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.5973 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1770 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.1648 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6504 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.7236 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8385 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8544 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8971 μM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.7292 μM | SANGER | |||
| U031 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8132 μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.0774 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.6455 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1155 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0015 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1793 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1026 μM | SANGER | |||
| P30-OHK | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1332 μM | SANGER | |||
| AN3-CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1615 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-257 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.79 μM | SANGER | |||
| MCF7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.8629 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4285 μM | SANGER | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4957 μM | SANGER | |||
| HGC-27 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1092 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.2895 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.9959 μM | SANGER | |||
| 786-0 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.65 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.0359 μM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.1778 μM | SANGER | |||
| EFM-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7533 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7806 μM | SANGER | |||
| UM-UC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.8059 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-29 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.8792 μM | SANGER | |||
| LN-405 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.0827 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.7726 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-502MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.9676 μM | SANGER | |||
| GMS-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.2974 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-JUSO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.347 μM | SANGER | |||
| insect cells | Function assay | Inhibition of N-terminal His-tagged BRAF V600E mutant (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells co-expressing CDC37 using biotinylated-MEK as substrate by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.013 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of BRAF V600E mutant in human A375 cells assessed as reduction in ERK phosphorylation by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.044 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of b-Raf in human A375 cells assessed phosphorylation of ERK, IC50 = 0.046 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human A375 cells expressing B-Raf V600E mutant and wild type Ras, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A375 cells harboring BRAF V600E mutant after 72 hrs by CellTiter-Glo assay, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 29461827 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells expressing wild type b-Raf and KRAS mutant, IC50 = 27 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur les lignées cellulaires | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 413.83 | Formule | C17H14ClF2N3O3S |
Stockage (À partir de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 918505-84-7 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | N/A | Smiles | CCCS(=O)(=O)NC1=C(C(=C(C=C1)F)C(=O)C2=CNC3=C2C=C(C=N3)Cl)F | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(200.56 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Entrez les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Entrez la formulation in vivo (Ceci nest que le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, ajouter ensuiteμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, ajouter ensuiteμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, ajouter ensuite μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, ajouter ensuite μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Remarque : 1. Assurez-vous que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue lors de lajout précédent est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
C-Raf-1 (Y340D/Y341D)
(Cell-free assay) 6.7 nM
B-Raf (V600E)
(Cell-free assay) 13 nM
BRK
(Cell-free assay) 130 nM
B-Raf
(Cell-free assay) 160 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
PLX-4720 présente une sélectivité >10 fois supérieure contre le B-Raf de type sauvage, et >100 fois supérieure contre d'autres kinases telles que Frk, Src, Fak, FGFR et Aurora A avec un IC50 de 1,3-3,4 μM. Ce composé inhibe significativement la phosphorylation de l'ERK dans les lignées cellulaires portant le B-RafV600E avec un IC50 de 14-46 nM, mais pas dans les cellules avec le B-Raf de type sauvage. Il inhibe significativement la croissance des lignées cellulaires tumorales portant l'oncogène B-RafV600E, telles que COLO205, A375, WM2664 et COLO829 avec un GI50 de 0,31 μM, 0,50 μM, 1,5 μM et 1,7 μM, respectivement. De plus, ce traitement chimique à 1 μM induit un arrêt du cycle cellulaire et une apoptose exclusivement dans les cellules 1205Lu B-RafV600E-positives, mais pas dans les cellules C8161 B-Raf de type sauvage. Ce traitement composé (10 μM) induit significativement une expression >14 fois de BIM dans les cellules PTEN+, par rapport aux lignées cellulaires PTEN- (4 fois), ce qui explique la résistance des cellules PTEN- à cette apoptose induite chimiquement.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Activités de la kinase Raf in vitro
|
|
Les activités de la kinase in vitro du Raf de type sauvage et de ses mutants sont déterminées en mesurant la phosphorylation de la protéine MEK biotinylée à l'aide de la technologie AlphaScreen de Perkin-Elmer. Pour chaque enzyme (0,1 ng), des réactions de 20 μL sont réalisées dans 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0,01% Tween-20, 100 nM de protéine MEK-biotine, diverses concentrations d'ATP et des concentrations croissantes de PLX-4720 à température ambiante. Les réactions sont arrêtées à 2, 5, 8, 10, 20 et 30 minutes avec 5 μL d'une solution contenant 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 200 mM NaCl, 80 mM EDTA et 0,3% de BSA. La solution d'arrêt comprend également l'anticorps phospho-MEK, des billes donneuses revêtues de streptavidine et des billes acceptrices de protéine A du kit de détection AlphaScreen Protein A. L'anticorps et les billes sont pré-incubés dans la solution d'arrêt dans l'obscurité à température ambiante pendant 30 minutes. La dilution finale de l'anticorps est de 1/2 000 et la concentration finale de chaque bille est de 10 μg/mL. Les plaques d'essai sont incubées à température ambiante pendant une heure puis lues sur un lecteur PerkinElmer AlphaQuest.
|
|
| In vivo |
L'administration orale de PLX-4720 à 20 mg/kg/jour induit des retards significatifs de croissance tumorale et des régressions dans les xénogreffes tumorales COLO205 dépendantes de B-RafV600E, sans effets indésirables apparents chez les souris, même à une dose de 1 g/kg. Ce composé à 100 mg/kg deux fois par jour élimine presque complètement les xénogreffes 1205Lu portant le B-RafV600E, tandis qu'il n'a aucune activité contre les xénogreffes C8161 portant le B-Raf de type sauvage. Les effets antitumoraux de ce composé sont corrélés au blocage de la voie MAPK dans les cellules hébergeant la mutation V600E. Ce traitement chimique à 30 mg/kg/jour inhibe significativement la croissance tumorale des xénogreffes 8505c de >90%, et diminue considérablement les métastases pulmonaires à distance.
|
Références |
|
Applications
| Méthodes | Biomarqueurs | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-FAK(S910) p-EGFR 1173 / EGFR / p-Akt / Akt p27 / Cyclin D1 / pRb pAkt(Ser473) / pAkt(Thr308) |
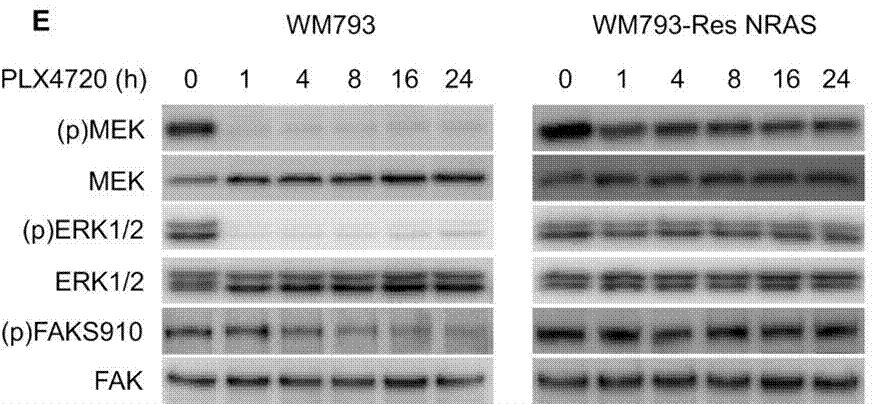
|
23076151 |
| Immunofluorescence | LAMP1 ZKSCAN3 / TFEB |
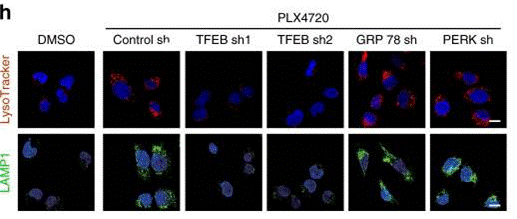
|
30979895 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
27848137 |
| ELISA | mIFN-γ |
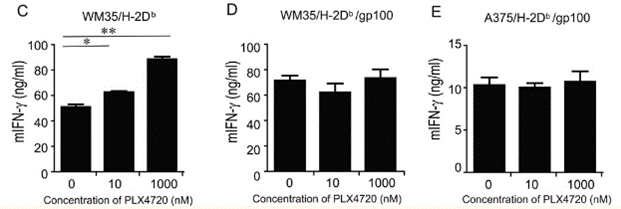
|
23204132 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
Questions fréquemment posées
Question 1:
What would you recommend to make working solution for intraperitoneal injection into mice?
Réponse :
Due to its very limited solubility in aqueous solution, this compound can be administered as a not fully dissolved suspension via oral gavage. For this reason, we recommend oral gavage for its administration.
